
With the increase in collective living spaces, fire risks are also increasing and therefore life and property safety issues are becoming more important. Therefore, like other fire-resistant products, fire-resistant cables have become an important part of our lives.
As it is known, many energy and signal cables used today have fire resistant types and are widely used in fire systems. With the increase in the technological levels of fire systems, it has become a need for fiber optic cables to be fire resistant.
According to the places of use, we can divide fire-resistant fiber optic cables into two groups:
With the increasing security elements in tunnels, subways and places such as industrial facilities where communication systems and video devices are used, the need and demand for fiber optic cables that must continue to function in the event of a fire is increasing day by day.
The most important feature that distinguishes fire-resistant fiber optic cables from other standard fiber optic cables is that they can continue their functions in the event of a fire. Another distinctive feature of these cables is the low smoke emission they emit during a fire. In this way, the risks of poisoning or suffocation from the smoke are minimized and life safety is carried to the highest level.
Sheath material used in fire-resistant fiber optic cables; LS0H are special materials called LSZH (Low Smoke, Zero Halogen), LSHF (Low Smoke, Halogen Free). The smoke emission of this type of material is much less than that of PVC and Polyethylene. In addition to the materials used, the design of the cable and its performance in the event of a fire are also decisive factors in the fire resistance criteria.
Fire-resistant fiber optic cables are suitable for use in pipes and for being buried directly in the ground (armored types).
Cable Structures
1- Armored (metallic) Fiber Optic Cables:


Dry essence: Rope or tape that swells in water is used to ensure water tightness. The reason why gel filling material is not preferred is to minimize smoke emission in case of any fire. For this reason, "dry essence" is recommended as the core structure in fire-resistant fiber optic cables.
Flame and heat barrier: Special tapes are used to reduce the effect of flame and heat on the inner layers of the cable and fiber tubes.
Reinforcement elements: Glass yarn is usually used. Glass yarns are used to meet the desired pulling force.
Inner cover: Special materials with low smoke emission and halogen-free are used.
Armor: It is usually covered with co-polymer material on both sides and used in corrugated steel tape. Thanks to the armor used, the cable core is protected from mechanical impacts and rodents.
Outer case: Special materials with low smoke emissions, halogen-free and resistant to environmental conditions are used.
2- Unarmored (non-metallic) Fiber Optic Cables:

Dry essence: The purpose of use and the materials used are the same as armored fiber optic cables.
Reinforcement elements: Glass yarn is usually used. Glass yarns are used to meet the desired pulling force. They also provide protection against rodents if they are used with a certain intensity.
Inner cover: Special materials with low smoke emission and halogen-free are used.
Outer case: Special materials with low smoke emissions, halogen-free and resistant to environmental conditions are used.
We can divide flame-resistant fiber optic cable tests into three main groups: Optical tests, mechanical tests and burn tests. The details of these tests, cable standards and specifications may vary according to customer demands. The basic tests are as follows:
Optical Tests (IEC 60793-1-40):
Cable attenuation measurement
Mechanical Tests (IEC 60794-1-2):
Cable tensile strength test (Tensile test – E1)
Crush test – E3
Impact test (E4)
Torsion test (Torsion test – E7)
Bending test (E11)
Temperature test (Temperature range – F1)
Water penetration – F5B
Fire Performance Tests:
IEC 60331-25, Continuing to function under flame:
The time it takes for the cables to continue their function under fire is tested. The cable is fixed horizontally to the test assembly as specified in the standard and the fibers are connected to the OTDR or Power Meter in a looping way. A temperature of 750°C is applied for a minimum of 90 minutes. After this process, the cooling process of 15 minutes is started. Fiber attenuation change is observed during flame application and cooling periods. During these two periods (flame application and cooling) there should be no breakage in the fiber.


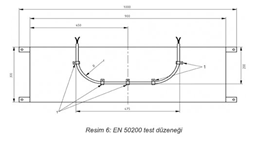
EN 50200, Continuing its function under flame and impact:
In the event of a fire, armored fiber optic cables are tested for resistance to external factors against falling particles or shaking. The sample to be tested must be a piece of cable of sufficient length (at least 5 m) with two ends coming out of the test cell and covered approximately 100 mm or with the outer covers removed at each end. For multiple fiber optic cables; The samples to be connected should be selected from the outermost layer of the cable.
If the length of the sample to be tested is not sufficient, identical fibers are connected to each end of the sample to provide sufficient length for the optical measurement method. Weight loss should be monitored for the duration of the test with OTDR or Power Meter.
During the test, an 830°C flame is applied to the cable and the device generating the sudden impact is activated. The sudden blow operation should blow at intervals of 5 minutes (±10 seconds). The applied impact time can be 30, 60, 90 or 120 minutes. At the end of this process, there should be no breakage in the fiber. According to this test result, cables are classified as pH30, pH60, pH90 or pH120 . The number after the pH statement shows how long the cable withstood the impact.
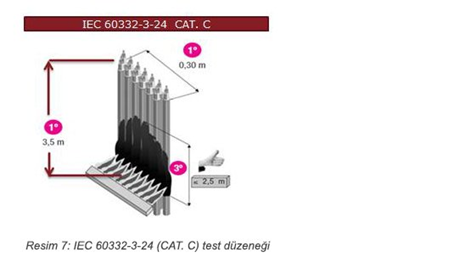
IEC 60332-3-24, Flame propulsion test for inspected cables:
According to the cable diameter, cable samples in the numbers and lengths specified in the standards are combined and flame is applied. The ≤ of flame advancement should be 2.5 m.
IEC 60754-1/2, Halogen acid gas test, acidic (corrosive) gas test:
It is applied to measure the corrosiveness of the gases released by the cables during combustion in terms of pH and conductivity. Required values: HCl < 0.5% pH ≥ 4.3 c ≤ 10μS/mm.
IEC 61034-2, Smoke density test:
According to the cable diameter, the light transmittance of the released smoke is measured by burning the number of cables specified in the standard in a closed cubic test chamber with a mixture of 90% ethanol, 4% methanol and 6% pure water in a closed cubic test chamber. The measurement result must be at least 60%.
These fire performance tests are the criteria to be applied to the cables on a type-by-type basis in order to continue to function in the event of a fire and to minimize the risks to life and property safety.
As Prysmian Group Turkey, our aim with our R&D studies is not only to develop new products or to reduce costs, but also to combine application-specific products with maximum performance and safety criteria. Our fire-resistant fiber optic cables that we have developed have all the performance and safety elements that are demanded or required for this type of cable. Our fiber optic cables, which complete the entire system along with energy and signal cables, have been developed as part of the entire system security. According to all changing demands and needs, we continue to develop our products.
 SİZİN DÜŞÜNCELERİNİZ?
SİZİN DÜŞÜNCELERİNİZ?