
Dr. Lecturer. Member.İsmail BOZKURT Marmara University
Input
In 1934, Italian scientist Enrico Fermi conducted experiments in Rome and found that neutrons could split most types of atoms. When uranium was bombarded with neutrons, it found atoms lighter than uranium instead of the elements it expected.
In Germany in 1938, Otto HAHN and Frittz Strassman were surprised to find lighter elements such as Barium-56 when they bombarded uranium with neutrons from a source containing radium and beryllium. To demonstrate their work, they took it to LisaMEITNER, an Australian scientist who had fled Nazi Germany. MEITNER was working with Otto R. FRISCH at the time. They thought that barium and other newly formed substances formed as a result of their experiments were substances formed by the splitting of uranium, but the atomic mass of the reacting material and the atomic mass of the products did not correspond to the atomic mass of the products. Then, using EINSTEN's formula E=m.c.c.c., they found the resulting energy output, thus proving the theory of both fission and the conversion of mass into energy. (1)
Summary
Energy is the necessary condition to ensure the continuation of economic activities in developed and developing countries.In our country, which made a leap in the industrial sector after the 1980s, energy supply has become a problem by increasing its importance.
The term nuclear energy was named 2. It was announced with the atomic bombs dropped on Nagasaki and Hiroshima during World War II. At the end of 1955, the USA and the USSR became the first countries to produce electricity from nuclear energy sources. In 1975, the construction of 157 power plants in 19 countries was completed. The oil-related energy crisis of the 1970s led energy-dependent countries to nuclear energy to a large extent. (2)
Nuclear Energy
Although it has serious dangers that can cause very serious environmental, economic, social and political problems in the event of a possible accident, nuclear energy is used especially by industrialized countries to meet increasing energy needs and to ensure the continuation of the growing economy. By 2030, nearly 200 new nuclear reactors are planned to be built in various countries of the world. While some of the countries are planning to build new nuclear power plants, some countries have taken decisions such as closing their existing power plants or banning the construction of nuclear power plants. As a result of the reactions of the people against nuclear energy among European countries, some countries have decided to close the existing nuclear power plants. In particular, concerns have increased about the reaction after the Fukushima nuclear accident and the safety risk of nuclear energy. As a matter of fact, Germany's closure of 8 reactors in 2011 and its declaration that it will close all nuclear reactors in the country until 2022 shows us that countries follow different policies on nuclear energy (3)
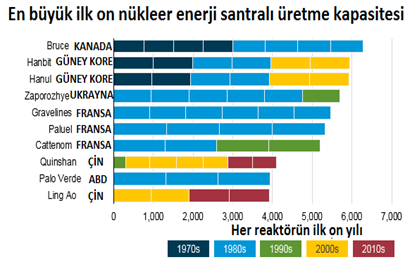
List of Top Ten Countries with the Most Nuclear Reactors
| COUNTRIES | Share in Electricity Generation (%) | Number of Nuclear Reactors | Number of reactors under construction |
| Us | 19% | 104 | 3 |
| France | 78% | 58 | 1 |
| Japan | 18% | 50 | 2 |
| Russia | 18% | 33 | 11 |
| South Korea | 35% | 23 | 4 |
| Canada | 15% | 20 | - |
| India | 4% | 20 | 7 |
| China | 2% | 16 | 28 |
| United Kingdom | 14% | 16 | - |
| Ukraine | 48% | 15 | 2 |
Bibliography: Ministry of Energy and Natural Resources of the Republic of Turkey.
What is the reason why industrialized and rapidly developing countries are increasingly using nuclear energy? The answer to this question should be sought primarily in the advantages provided by nuclear energy and in the fact that fossil energy, which meets a significant part of the energy needs, is at risk of depletion. The fact that the need for energy will exist as long as human life continues and that fossil energy sources are at risk of rapid depletion has led to the fact that states turn to alternative energies such as nuclear energy or renewable energy sources.
Distribution of Electricity Produced in the World According to Energy Resources
| Energy Resources | World |
| Oil | 4,60% |
| Natural gas | 22,20% |
| Coal | 40,60% |
| Hydraulic | 16,00% |
| Nuclear | 13,00% |
| Other (Renewable, etc.) | 3,70% |
| sum | 21,431 TWh |
Bibliography: Ministry of Energy and Natural Resources of the Republic of Turkey.
Turkey's Nuclear Energy Policy
In order to meet the increasing energy need in Turkey, it has turned its energy policy to nuclear energy. Since Turkey does not have the nuclear technology that countries such as the USA, Japan or Russia have, it carries out the construction of nuclear reactors through imports. The fact that nuclear energy, which requires advanced technology, is under construction in Turkey has brought with it very serious discussions.
Turkey, which plans to become one of the world's 10 largest economies by 2023, has started to develop new energy policies in order to have energy resources to support its economic goals, to end its dependence on foreign energy and to alleviate the economic burden caused by excessive energy exports. At the beginning of these policies, the use of nuclear energy by reducing dependence on energy sources such as coal, oil and natural gas, which are fossil energy sources, comes. When we look at the other side of the coin, that is, the disadvantages of nuclear energy, which is seen as very attractive when we look only at its advantages, we are faced with a very different picture.
Nuclear energy, which has caused different debates among both the media and scientists, constitutes the center of Turkey's new energy policies. Turkey, which is under construction of nuclear power plants, has made its decision as a result of long efforts on the choice of location. The nuclear power plants decided to be built in Mersin, Sinop and finally Kırklareli provinces have been frequently discussed by the local people. Especially due to its proximity to Istanbul, the nuclear power plant planned to be built in Kırklareli is exposed to serious reactions despite the possible risk of accidents. (3)
Positive-Negative Aspects of Nuclear Energy
Ideas about the advantages of nuclear energy can be expressed as follows:
Despite these advantages of nuclear energy, there are many negative aspects if they are counted:
.
Result
Although Turkey has various primary energy resources, it cannot benefit from these resources sufficiently, cannot provide efficiency in energy production and transmission, and does not give due importance to the issue of loss-leakage. The low share of renewable energy among energy sources, the lack of serious and decisive steps towards the installation of nuclear power plants lead to inadequacy in resource diversity and maintain external dependence on energy.
Turkey, which is dependent on foreign countries, sees nuclear energy as an alternative option in order to close its energy deficit. Before the construction of nuclear facilities, the conditions in Turkey and the risks of accidents in these facilities and the developments that may occur after them should be taken into consideration.
 SİZİN DÜŞÜNCELERİNİZ?
SİZİN DÜŞÜNCELERİNİZ?